プロトアクチニウム
91
Pa
族
該当なし
周期
7
ブロック
f
陽子
電子
中性子
91
91
140
一般特性
原子番号
91
原子量
231.03588
質量数
231
カテゴリ
アクチノイド
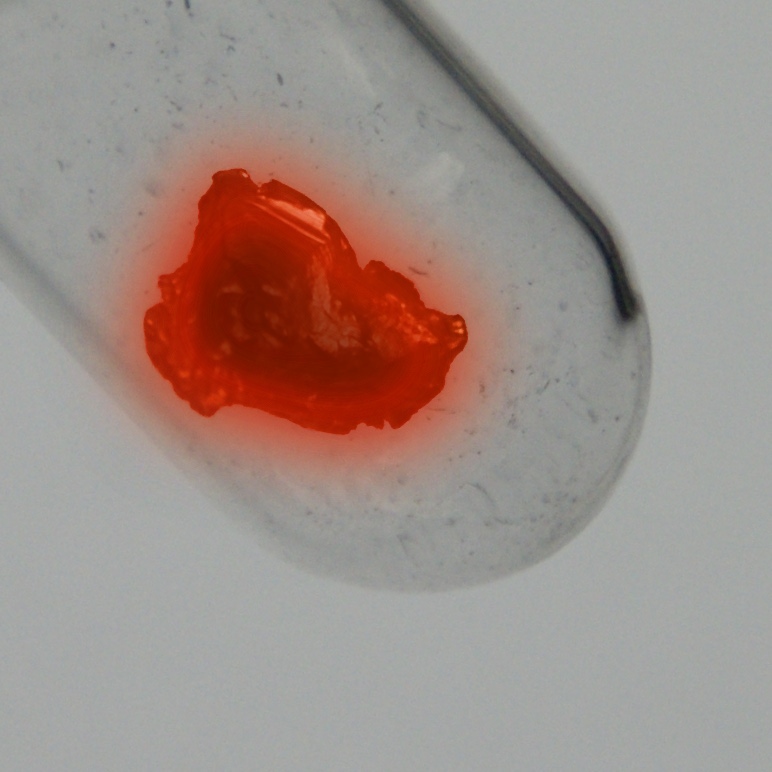
色
銀色
放射性
はい
From the Greek protos meaning first
結晶構造
体心 正方晶系
歴史
In 1900, William Crookes isolated protactinium as an intensely radioactive material from uranium
Protactinium was first identified in 1913 by Kasimir Fajans and Oswald Helmuth Göhring in Germany.
A more stable isotope of protactinium was discovered in 1917 by Otto Hahn and Lise Meitner at the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute in Berlin.
Protactinium was first identified in 1913 by Kasimir Fajans and Oswald Helmuth Göhring in Germany.
A more stable isotope of protactinium was discovered in 1917 by Otto Hahn and Lise Meitner at the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute in Berlin.
電子殻
2, 8, 18, 32, 20, 9, 2
電子配置
[Rn] 5f2 6d1 7s2
Protactinium is one of the rarest and most expensive naturally occurring elements
物理特性
相
固体
密度
15.37 g/㎝3
融点
1841.15 K | 1568 °C | 2854.4 °F
沸点
4300.15 K | 4027 °C | 7280.6 °F
融解熱
15 kJ/mol
蒸発熱
470 kJ/mol
熱容量
-
地殻中における存在比
9.9×10-13%
宇宙空間における存在比
該当なし
CAS登録番号
7440-13-3
PubChem CID番号
該当なし
原子特性
原子半径
163 pm
共有結合半径
200 pm
電気陰性度
1.5 (ポーリングの値)
イオン化エネルギー
5.89 eV
モル体積
15.0 ㎝3/mol
熱伝導率
0.47 W/㎝·K
酸化数
3, 4, 5
用途
Owing to its scarcity, high radioactivity and high toxicity, there are currently no uses for protactinium outside of scientific research.
With the advent of highly sensitive mass spectrometers, an application of 231Pa as a tracer in geology and paleoceanography has become possible.
Protactinium-231 combined with the thorium-230 can be used to date marine sediments.
With the advent of highly sensitive mass spectrometers, an application of 231Pa as a tracer in geology and paleoceanography has become possible.
Protactinium-231 combined with the thorium-230 can be used to date marine sediments.
Protactinium is toxic and highly radioactive
同位体
安定同位体
-不安定同位体
212Pa, 213Pa, 214Pa, 215Pa, 216Pa, 217Pa, 218Pa, 219Pa, 220Pa, 221Pa, 222Pa, 223Pa, 224Pa, 225Pa, 226Pa, 227Pa, 228Pa, 229Pa, 230Pa, 231Pa, 232Pa, 233Pa, 234Pa, 235Pa, 236Pa, 237Pa, 238Pa, 239Pa, 240Pa