アクチニウム
89
Ac
族
該当なし
周期
7
ブロック
f
陽子
電子
中性子
89
89
138
一般特性
原子番号
89
原子量
[227]
質量数
227
カテゴリ
アクチノイド
色
銀色
放射性
はい
From the Greek aktis, aktinos, meaning beam or ray
結晶構造
面心立方格子
歴史
André-Louis Debierne, a French chemist, discovered actinium in 1899.
He separated it from pitchblende residues left by Marie and Pierre Curie after they had extracted radium.
Friedrich Oskar Giesel independently discovered actinium in 1902 as a substance being similar to lanthanum.
He separated it from pitchblende residues left by Marie and Pierre Curie after they had extracted radium.
Friedrich Oskar Giesel independently discovered actinium in 1902 as a substance being similar to lanthanum.
電子殻
2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 9, 2
電子配置
[Rn] 6d1 7s2
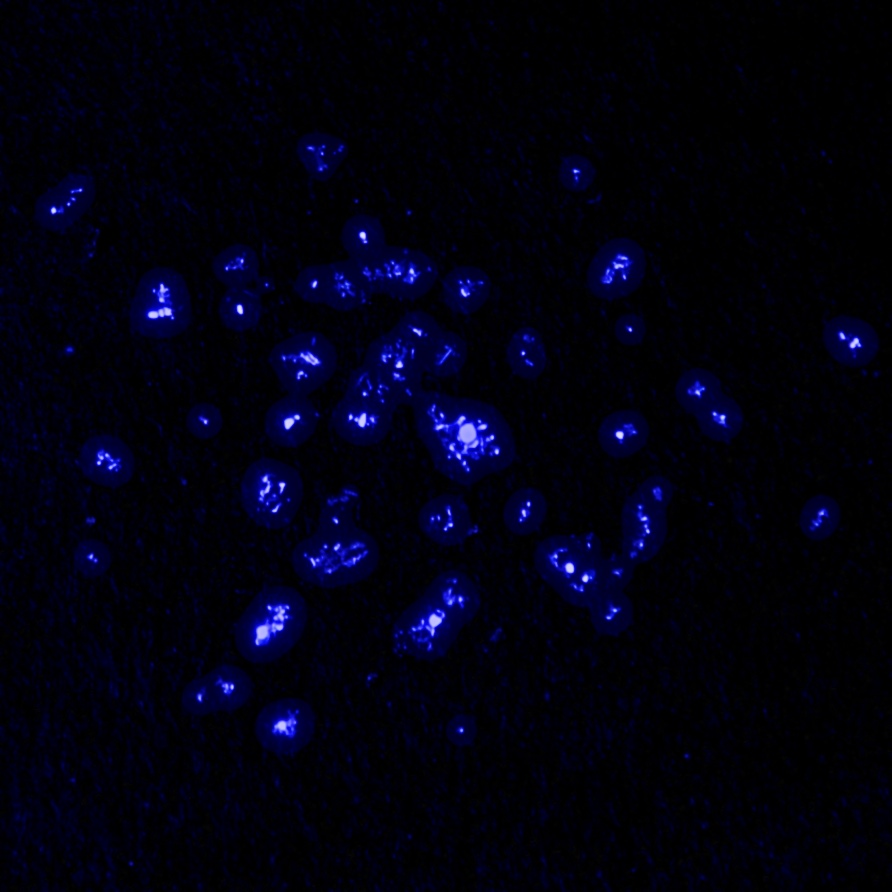
Actinium glows in the dark with a pale blue light
物理特性
相
固体
密度
10.07 g/㎝3
融点
1323.15 K | 1050 °C | 1922 °F
沸点
3471.15 K | 3198 °C | 5788.4 °F
融解熱
14 kJ/mol
蒸発熱
400 kJ/mol
熱容量
0.12 J/g·K
地殻中における存在比
該当なし
宇宙空間における存在比
該当なし
CAS登録番号
7440-34-8
PubChem CID番号
該当なし
原子特性
原子半径
-
共有結合半径
215 pm
電気陰性度
1.1 (ポーリングの値)
イオン化エネルギー
5.17 eV
モル体積
22.54 ㎝3/mol
熱伝導率
0.12 W/㎝·K
酸化数
3
用途
Actinium is used as an active element of radioisotope thermoelectric generators, for example in spacecraft.
The medium half-life of 227Ac makes it very convenient radioactive isotope in modeling the slow vertical mixing of oceanic waters.
225Ac is applied in medicine to produce 213Bi in a reusable generator or can be used alone as an agent for radiation therapy.
The medium half-life of 227Ac makes it very convenient radioactive isotope in modeling the slow vertical mixing of oceanic waters.
225Ac is applied in medicine to produce 213Bi in a reusable generator or can be used alone as an agent for radiation therapy.
Actinium is highly radioactive
同位体
安定同位体
-不安定同位体
206Ac, 207Ac, 208Ac, 209Ac, 210Ac, 211Ac, 212Ac, 213Ac, 214Ac, 215Ac, 216Ac, 217Ac, 218Ac, 219Ac, 220Ac, 221Ac, 222Ac, 223Ac, 224Ac, 225Ac, 226Ac, 227Ac, 228Ac, 229Ac, 230Ac, 231Ac, 232Ac, 233Ac, 234Ac, 235Ac, 236Ac